Integrity of Long RNA
Digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) is an invaluable tool for determining whether long nucleic acid molecules remain intact after processes such as enzymatic reactions or viral nucleic acid replication. This capability is particularly useful for studies involving complex molecular structures, like self-amplifying RNA (saRNA).
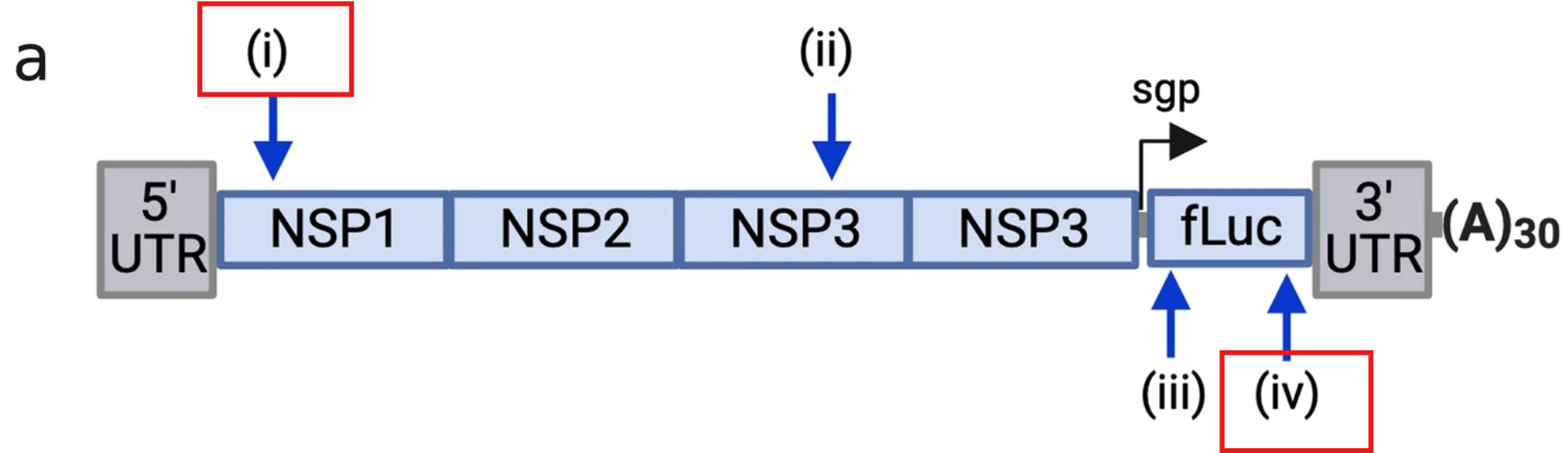
A recent study by Casmil et al., 2023 demonstrated how ddPCR can quantify the percentage of intact saRNA molecules following reverse transcription in vitro. This approach relies on designing primers and probes targeting the terminal regions of the saRNA molecules after they are reverse-transcribed into copy DNA (cDNA).
Method Overview The researchers developed a duplex ddPCR assay targeting two specific loci—designated as (i) and (iv)—at opposite ends of the saRNA molecule. This assay was employed to determine the percentage of full-length saRNA molecules after reverse transcription, comparing the results obtained from one-step versus two-step ddPCR protocols.
- Primer and Probe Design:
- Probes were designed for loci (i) and (iv), representing the 5’ and 3’ ends of the saRNA.
- FAM and HEX fluorophores were used to distinguish these regions.
- Duplex ddPCR Assay:
- The assay was performed under optimized conditions to maximize the accuracy of detecting molecules containing both loci.
- Samples were analyzed for the presence of double-positive droplets (containing both FAM and HEX signals) versus single-positive droplets (containing only one fluorophore signal).
 source: Casmil et al., 2023, Figure 1
source: Casmil et al., 2023, Figure 1
Assessing Molecular Integrity
The integrity of reverse-transcribed saRNA molecules was determined by evaluating droplet patterns:
-
Double-positive droplets (FAM + HEX):
These represent molecules where both loci (i) and (iv) are present, indicating that the saRNA remained intact throughout reverse transcription.
-
Single-positive droplets (FAM-only or HEX-only):
These indicate partial reverse transcription, where only one terminal region of the molecule was successfully reverse transcribed.
By quantifying the proportion of double-positive droplets relative to the total droplets, the researchers were able to calculate the percentage of intact saRNA molecules. This method offers a robust way to assess the fidelity of enzymatic or synthetic processes involved in RNA manipulation.