Wastewater Monitoring
An interesting preprint by Balogh et al., 2024 presents a comprehensive approach to wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance. Conducted over 32 months at a major metropolitan wastewater treatment plant, the study demonstrates the efficacy of combining a novel RNA extraction method with reverse transcription-droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) and targeted mutation assays to monitor viral load and variant dynamics in the community.
This study combined the following approach(es) to assess the viral/variant dynamics in the community:
- Two-Step Direct Capture RNA Extraction -> Integration with RT-ddPCR to monitor for absolute quantification of viral RNA
- Targeted Mutation Assays to delineate between different SARS-CoV-2 variants circulating in the population
- Longitudinal Surveillance period ensured a comprehensive view of viral load fluctuations and variant dynamics
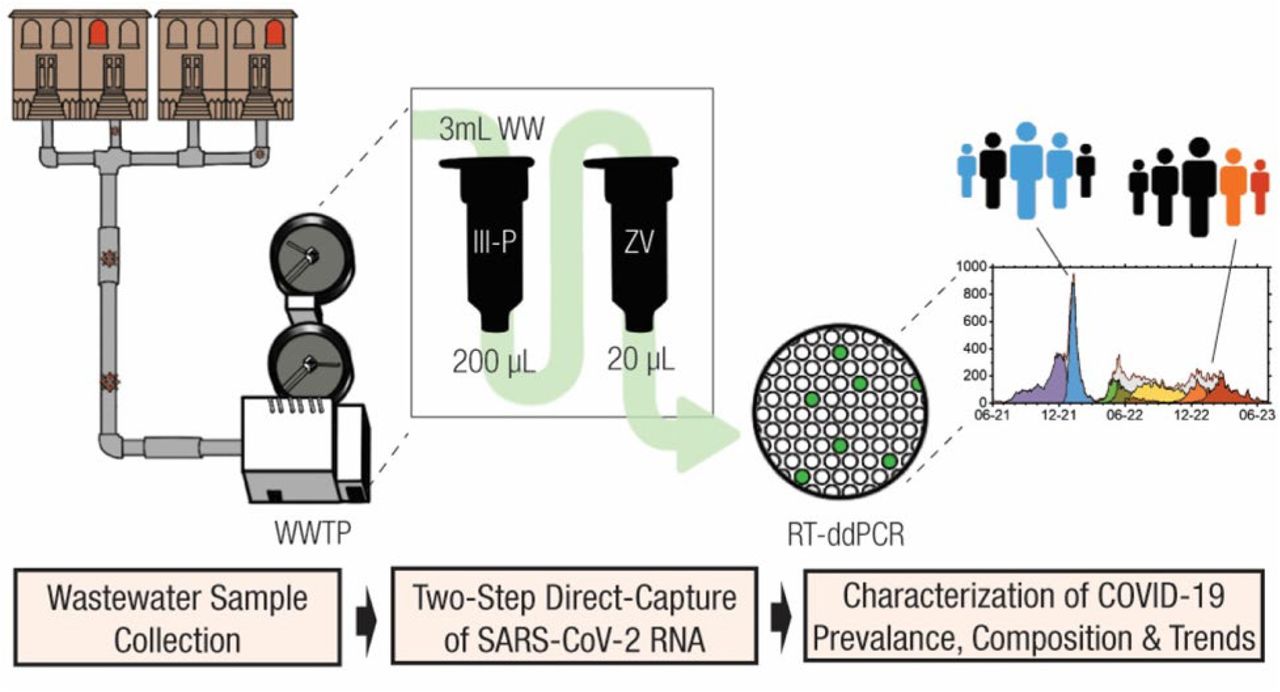
source: Balogh et al., 2024, Graphical abstract
This study highlights the potential of RT-ddPCR-based wastewater surveillance as a powerful tool for public health monitoring. Specifically, it can:
-
Monitor Infected Populations: By quantifying viral RNA in wastewater, health authorities can estimate infection levels in the community, including asymptomatic cases.
-
Delineate Circulating Serotypes: Targeted mutation assays enable the identification and tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants, informing on the spread and dominance of specific strains.
-
Predict Outbreaks: Early detection of increases in viral load or the emergence of new variants can serve as a warning system, allowing for timely interventions.
Another impressive study from an optimization and multiplexing perspective was performed and published by Zafeiriadou et al., 2025.
In this paper, the authors developed a 9-plex Multiplex One-Step RT-ddPCR assay to detect 9 targets in a single well (6 viral targets - SARS-CoV2 N1&N2, Influenza A M gene, Influenza B NS gene, RSV M gene, Hep A 5UTR, Hep E ORF3; 3 controls - B2M endogenous, IC endogenous & EC).
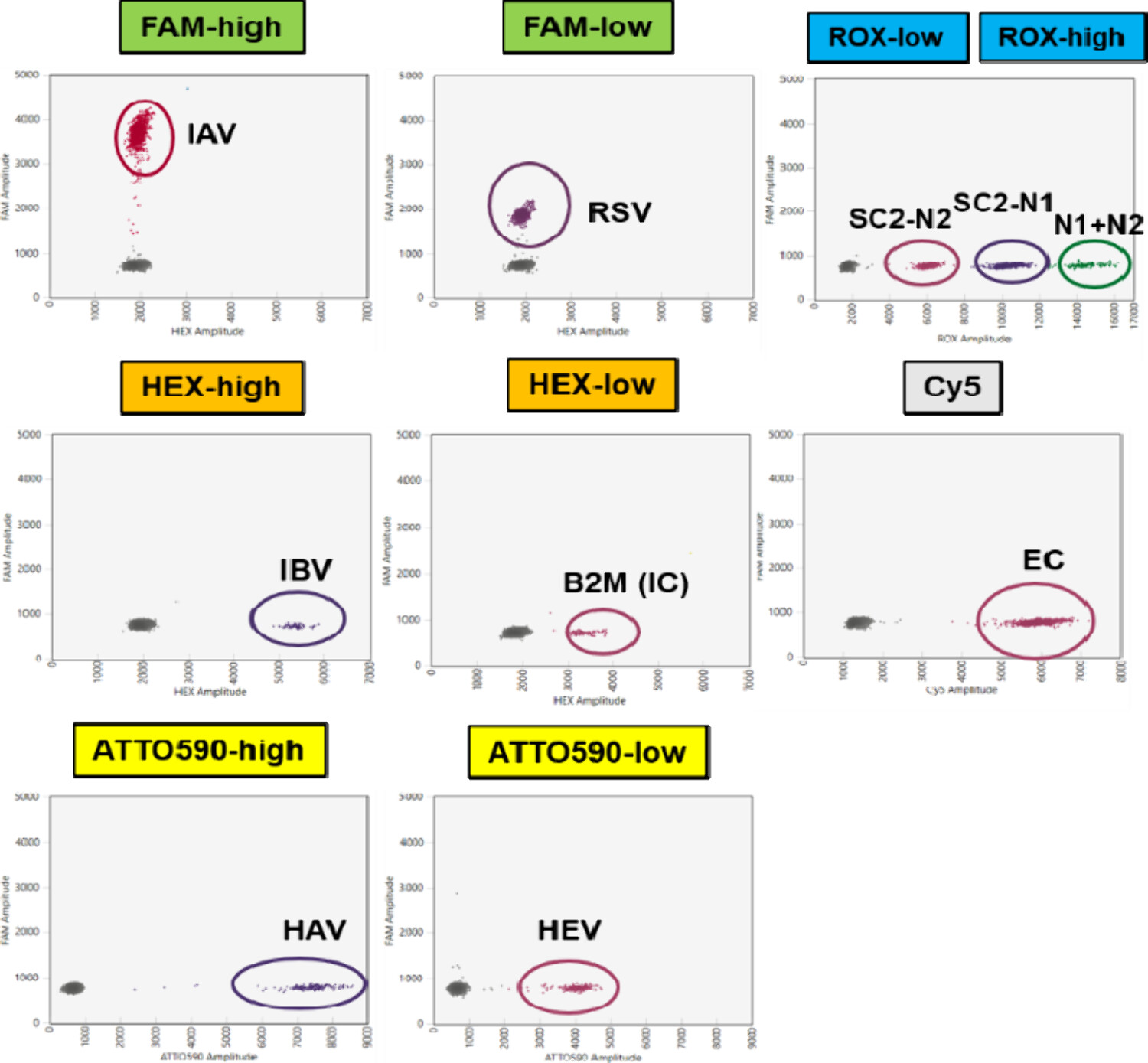
source: Zafeiriadou et al., 2025, Figure 2
The most surprising finding was how little optimization needed to be done (adjusting annealing temp, extension time & concentrations of the primes & probes).
The LOD value was set at 2.2 (95% CI: 1.7−2.7), 2.0 (95% CI: 1.6−2.4), 1.4 (95% CI: 1.1−1.7), 2.1 (95% CI: 1.7−2.4), 2.9 (95% CI: 2.4−3.3), 1.8 (95% CI: 1.4−2.2) and 1.9 (95% CI: 1.6−2.2) copies/μL of sample input for SARS-CoV-2 N1 gene, N2 gene, IAV, IBV, RSV, HAV, and HEV, respectively.
LOQ was set as the lowest detected concentration that had a coefficient of variation (CV) ≤ 25 and was set at 5.8, 6.1, 3.46, 5.45, 5.89, 6.14, and 4.61 copies/μL for SARS-CoV-2 N1 gene, N2 gene, IAV, IBV, RSV, HAV, and HEV, respectively.