Single Cell Mutant RNA Enrichment
To achieve highly specific detection of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) oligos can be utilized. A notable example is demonstrated in a study by Sun et al., 2018. In this study, the authors developed an assay to detect the BRAF V600E mutation—a site-specific alteration strongly associated with melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer—in the mRNA of single cells using PNA probes designed for highly specific binding.
The Principle
PNA binds tightly to wild-type RNA, forming a stable duplex that completely inhibits the subsequent reverse transcription ddPCR (RT-ddPCR). As a result, droplets containing wtRNA remain fluorescence-negative. In contrast, PNA does not form a stable duplex with mutant RNA (mutRNA) due to a single-base mismatch. This allows RT-ddPCR to proceed, generating fluorescence-positive droplets that indicate the presence of mutant RNA. (See the image below for a visual representation of the workflow.)
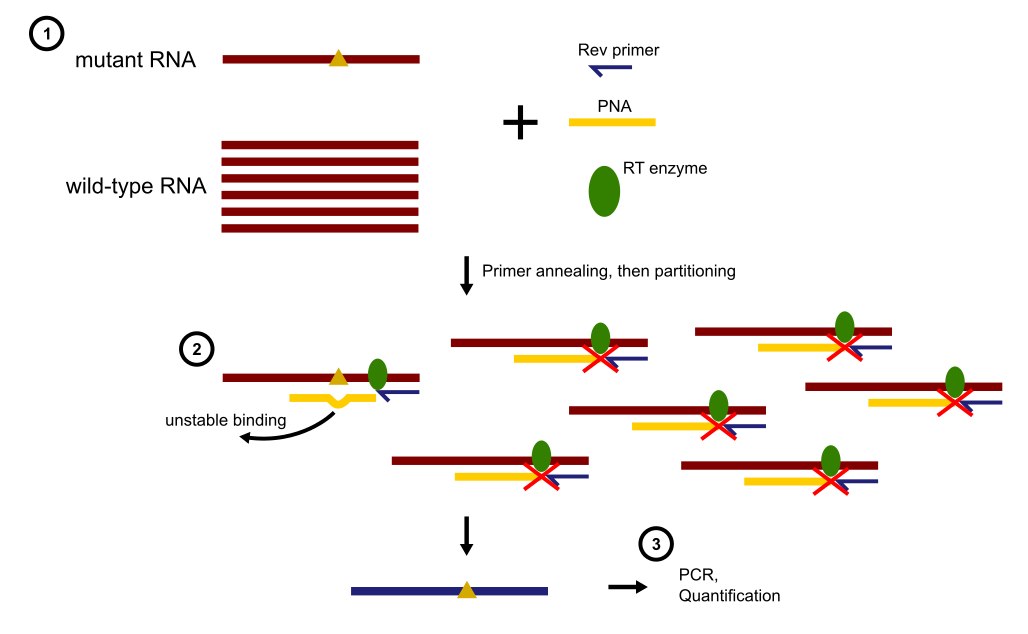 Diagram illustrating the PNA clamping mechanism leading to mutant RNA enrichment
Diagram illustrating the PNA clamping mechanism leading to mutant RNA enrichment
The makeup of the PNA
The PNA used in the study was a 16-nt PNA sequence (with 5’ and 3’ replaced with N’ and C’ termini), which exhibits excellent ability to distinguish singe-base variation, is designed to be complementary to the wtRNA with a melting temperature (Tm) of ∼70 °C. In contrast, the PNA/mutRNA duplex with a mismatch site in the middle of the sequence has an approximately 10−20 °C lower Tm than that of the PNA/ wtRNA.
The General Workflow
The reverse primer, RT buffer, dNTPs and target mRNAs (or cell lysate) were mixed, heated (denature RNA and dissolve secondary structures), and then incubated at a constant temperature (primer annealing).
Afterward, the mixture was put on ice, and the forward primer, PNA, Taqman probe, Ribonuclease inhibitor, reverse transcriptase (SSIV), and supermix were further introduced to make a final 20 μL volume for ddRT-PCR.
The ddRT-PCR was performed employing a simple one step RT-ddPCR protocol.
PNA clamps are useful in very sensitive and precise detection and quantification of SNVs in RNA molecules, by actively enriching for mutRNA molecules (and in turn blocking the reverse transcription of wtRNA).