Ligation Probes for miRNA Quantification
miRNAs are short RNA molecules (~20 nucleotides) that pose unique challenges for detection and quantification using PCR. Their small size provides limited binding regions for reverse transcription (RT) primers, complicating the RT step. Additionally, the low melting temperature (Tm) of RT primers can reduce the efficiency of the RT reaction and lead to a low signal-to-noise ratio.
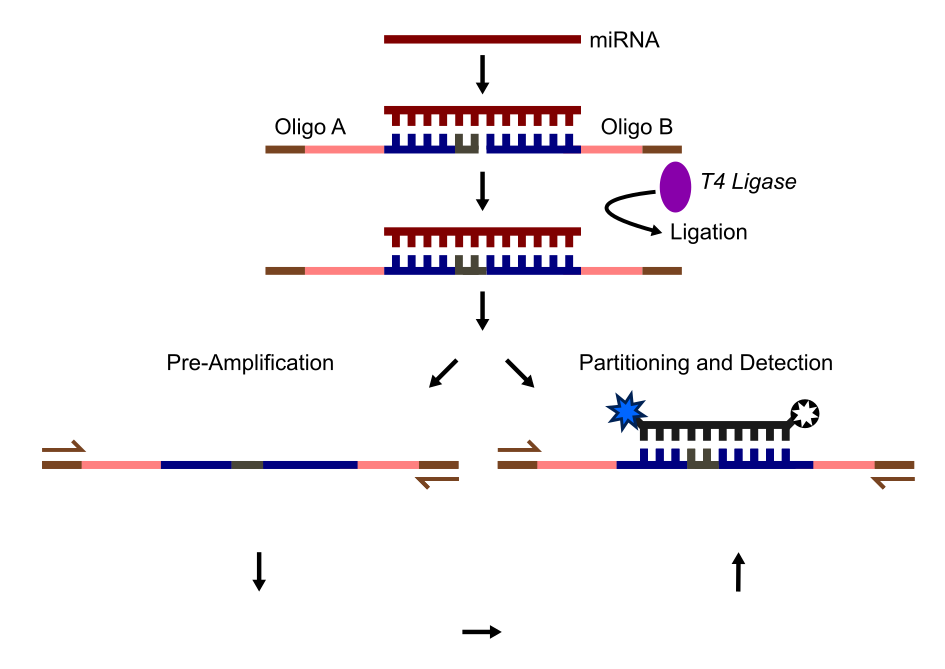
A novel solution to these challenges is presented in the paper by Tian et al., 2016. The authors developed an alternative digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) method to quantify specific miRNAs, even from single cells. Their approach avoids the delicate RT conditions by using two custom-designed DNA oligos, A and B, which partially overlap with the miRNA sequence. These oligos anneal to the miRNA and are ligated to form a single DNA molecule.
Once ligated, the DNA amplicons are partitioned into droplets, amplified, and detected using TaqMan probes and primers. Oligos A and B are designed to include complementary binding regions for the miRNA (which serve as the TaqMan probe binding site after ligation) and upstream primer binding sites. This customizable design supports multiplexing and eliminates the need for RT to generate cDNA. It can also detect miRNA with minor mutations, albeit with slightly lower efficiency, directly from single-cell lysates.
The diagram below illustrates the detection and quantification workflow of this miRNA ddPCR method:
- Annealing and ligation: Oligos A and B bind complementary regions of the miRNA and are ligated to form a full amplicon.
- Optional: Ligated amplicon(s) can be pre-amplified prior to ddPCR using the terminal primer binding sites (sequences in brown).
- Partitioning and detection: The ligated amplicons are partitioned into droplets. Primer pairs amplify the amplicons, and a TaqMan probe binds to the overlap region of Oligos A and B for detection.
- Droplet analysis: Droplets are classified as positive or negative based on the presence of fully formed amplicons (not shown).
 Example workflow based on Tian et al., 2016 for specific miRNA detection at a single cell level
Example workflow based on Tian et al., 2016 for specific miRNA detection at a single cell level
This approach offers a robust and efficient method for miRNA quantification, even in challenging sample types like single-cell lysates.